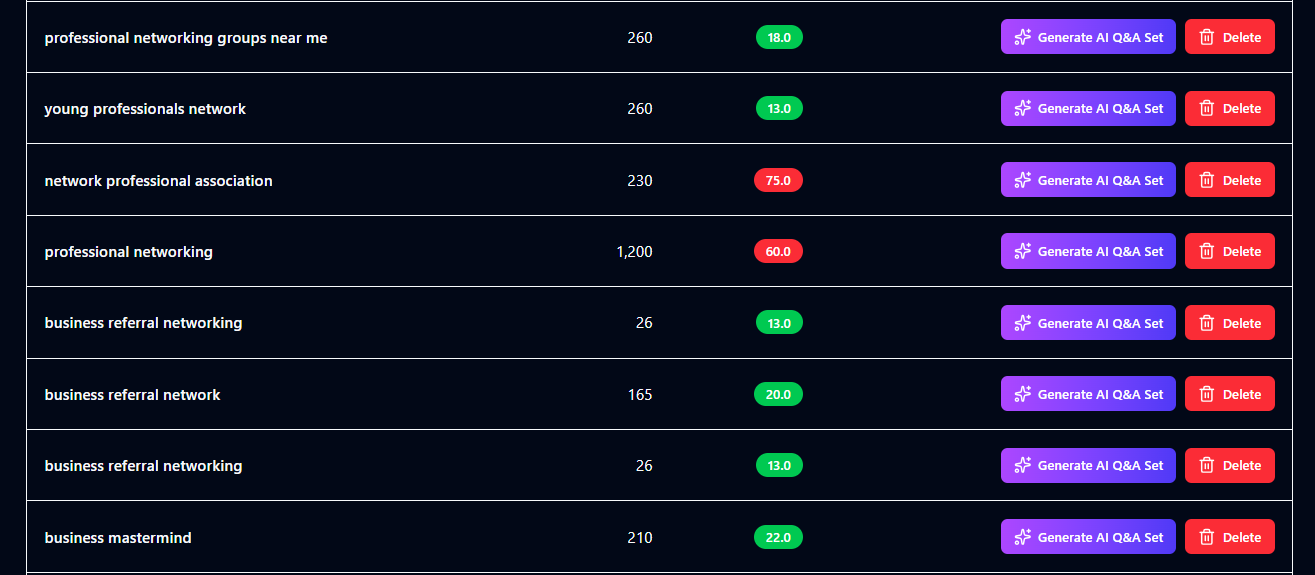
If you're targeting Perplexity, search your question and look at what gets cited. If targeting ChatGPT, use Temporary Chat mode. Study:
- What topics do all the top results cover?
- What do they skip or gloss over?
- What perspective do they take?
- What format are they in?
- How recent is the information?
Identify Content Gaps
Look for:
- Specific subtopics mentioned briefly but not explored deeply
- Perspectives not represented (beginner vs. advanced, industry-specific, demographic-specific)
- Missing data, examples, or case studies
- Outdated information that needs 2025 updates
- Questions in comments or forums that the content doesn't answer
Use Your Unique Expertise
What do you know that others don't? This could be:
- Personal experience with the problem
- Professional expertise in a niche
- Access to proprietary data or research
- Unique methodology or framework
- Case studies from real clients
- Technical knowledge others lack
Think About Alternative Formats
Sometimes the differentiation isn't just the angle—it's the format:
- Landing page with specific information instead of a blog post
- Interactive tool or calculator
- Comprehensive comparison table with unique criteria
- Step by step template or checklist
- Video walkthrough embedded with transcript
- Original research or survey results
Real Example: The Xanadu Case Study
Let me share a concrete example of the blue ocean approach in action.
The Challenge:
My previous startup GoBrunch (a virtual event platform) wanted to rank for terms related to community platforms. But the keyword "community platforms" and related terms are dominated by high-authority sites like:
- G2 (DR 90 plus)
- Capterra (DR 90 plus)
- TechCrunch articles
- Established SaaS blogs
Writing yet another "Top 10 Community Platforms" article would be pointless. It would disappear into the noise.
The Traditional Approach:
Create a more comprehensive comparison article, add more features to the table, make it longer, add more screenshots. Compete directly with sites that have 10x the domain authority.
The Blue Ocean Strategy:
Instead of writing about community platforms broadly, write about the Xanadu color—a specific shade of blue-green that resonates with creative professionals.
Why This Worked:
- Lower Difficulty: Keyword difficulty was below 10 (versus 60 plus for community platform terms)
- Aligned with Audience: GoBrunch's target audience is creative professionals who care about aesthetics and color
- Unique Angle: Nobody else was comprehensively covering Xanadu as a color choice for creative digital spaces
- Expertise Fit: The platform could showcase how they implemented this color philosophy
- Reduced Competition: Instead of competing with 1,000 articles about community platforms, there were maybe 10 decent articles about the Xanadu color
The Results:
- Ranked in top 5 on Google
- Cited in Perplexity results
- Brought qualified traffic (creative professionals who care about design)
- Established thought leadership in an unexpected area
The Lesson:
Don't fight where everyone else is fighting. Find the adjacent topic that serves your audience but has minimal competition.
Ways to Differentiate Your Content
Original Research or Data
- Survey your customers
- Analyze industry trends from your unique position
- Compile data nobody else has access to
- Share proprietary metrics or benchmarks
Unique Visual Content
- Custom infographics with your methodology
- Original diagrams or frameworks
- Before and after case studies
- Process visualizations
- Interactive tools
Specific Use Case Focus
- Industry-specific guides (e.g., "for real estate agents" not just "for businesses")
- Demographic-specific content (e.g., "for single women" not just "for people")
- Situation-specific solutions (e.g., "for people who don't respond to steroids")
Proprietary Methodology
- Your unique framework or process
- A system you've developed and tested
- Step by step approach that's different from standard advice
Expert Interviews or Perspectives
- Insights from practitioners in your field
- Contrarian viewpoints backed by experience
- Multiple expert perspectives synthesized
Interactive Tools or Calculators
- ROI calculators
- Assessment tools
- Interactive decision trees
- Comparison generators
Niche Sub-Topics
- Go deep on one aspect rather than broad overview
- Cover the 5% that others skip
- Address edge cases or special circumstances
Content Format Considerations
Remember: sometimes it's not even a blog article. The best format depends on the query intent:
Landing Page: When people want specific product or service information
Blog Post: For how-to, explanatory, or educational content
Comparison Page: For evaluation and decision-making queries
Tool or Calculator: For quantitative problems
Checklist or Template: For process-oriented queries
Video plus Transcript: For visual learners and accessibility
Your Action Step
For your priority question, answer these:
- What are the top 3 to 5 sources currently cited?
- What do they all have in common (the "red ocean")?
- What gap or angle are they missing?
- What unique expertise or resource do I have?
- What would make my content impossible to ignore?
Write down your differentiation strategy in one sentence: "Unlike existing content which focuses on X, my content will Y because Z."
This sentence will guide everything you create in Step 7.
Step 7: Content Creation
Now you're ready to create content that actually ranks. You have your question, your differentiation strategy, and your research. This step is about execution.
Phase 1: Outline Development
Start with an outline before writing. This structure will keep you focused on your differentiation strategy.
Using AI to Create Your Outline
AI can be incredibly helpful here, but you need to be strategic about your prompt:
Bad prompt: "Create an outline for an article about treating scalp psoriasis"
Good prompt: "Create an outline for an article answering 'How to treat mild scalp psoriasis at home in 2025 for people who don't respond well to steroids.' The unique angle of this article is [your differentiation strategy]. The target audience is [your persona]. Include sections that address [specific gaps you identified]."
Critical: The AI must understand what makes your content different. If you don't communicate your unique angle, the AI will generate a generic outline that looks like everything else.
Phase 2: Writing the Content
You can use AI to draft sections, but here's the non-negotiable rule: your unique expertise and perspective must shine through.
AI should assist, not replace, your knowledge. Think of it this way:
- AI provides structure and helps articulate ideas
- You provide the insights, experience, and expertise
- The combination is what wins citations
Phase 3: Mandatory Elements (Based on Research)
Our research into AI citation patterns shows that certain elements consistently improve your chances of being cited. Include all of these:
✅ Fresh Date at the Beginning
Add either:
- Publication date: "Published: November 18, 2025"
- Last updated: "Last Updated: November 18, 2025"
- Or both
Place this prominently near the title. AI engines especially Perplxity use freshness as a ranking signal, especially for queries with year indicators.
✅ Clear H1 Tag
Your main title should be in an H1 tag. Make it match the question you're targeting:
- If the question is "How to treat mild scalp psoriasis at home in 2025 for people who don't respond well to steroids?"
- Your H1 could be: "How to Treat Mild Scalp Psoriasis at Home: A 2025 Guide for Steroid Non-Responders"
✅ Strategic H2 Structure
Break your content into clear sections with descriptive H2 headings. AI engines parse structure to understand content hierarchy.
Good H2 examples:
- "Why Standard Steroid Treatments Don't Work for Everyone"
- "5 Evidence-Based Home Remedies for Mild Scalp Psoriasis"
- "Creating Your Personalized Treatment Protocol"
Bad H2 examples:
- "Introduction"
- "Methods"
- "More Information"
✅ Bullet Points for Scannability
Use bullet points to break up dense information. AI engines can more easily parse and cite specific points when they're formatted as lists.
Use bullets for:
- Lists of options or alternatives
- Step-by-step processes
- Key takeaways
- Feature comparisons
- Pros and cons
✅ FAQ Section
Include a dedicated FAQ section answering related questions. This serves multiple purposes:
- Captures long-tail variations of your main question
- Provides quotable, citation-friendly snippets
- Improves content comprehensiveness
- Signals expertise through anticipating questions
✅ TL;DR for Question-Format Titles
If your title is a question, add a TL;DR (Too Long; Didn't Read) summary at the top, right after the title and date.
This gives AI engines a concise, citation-ready answer to extract.
Phase 4: Visual Elements - The HTML Advantage
This is where you can create a significant competitive advantage. Most content creators still export charts from Excel as PNG files. You're going to do something smarter.
Why HTML Visualizations Beat Traditional Images
When you embed a table or chart as an image:
- AI engines can't read the data
- Search engines can't index the information
- The text isn't searchable
- Users can't copy or interact with data
- Mobile responsiveness is limited
When you use HTML visualizations:
- ✅ Searchable: Text in HTML is readable by AI engines
- ✅ Indexable: Search engines can parse and understand the data
- ✅ Accessible: Screen readers and AI can access the information
- ✅ Responsive: Automatically adapts to different screen sizes
- ✅ Lightweight: Faster page load times than images
- ✅ Editable: Easy to update without graphic design tools
The Game-Changing Shift
Instead of: Creating a comparison table in Excel, taking a screenshot, uploading as PNG
Do this: Ask AI to create an HTML visualization you can embed directly
How to Create HTML Visualizations
Step 1: Describe What You Want
Be specific about the data and format. Example prompts:
"Create an HTML table comparing these 5 CRM platforms: [list platforms]. Include columns for pricing, key features, best for (use case), and pros/cons. Make it visually appealing with CSS styling that I can preview."
"Generate an interactive HTML comparison chart for these project management tools with sortable columns for price, team size, and key features."
"Build an HTML timeline visualization showing the evolution of AI search engines from 2023-2025, with major milestones for ChatGPT, Perplexity, Gemini, Claude, and Grok."
Step 2: Request HTML Format
Always specify you want HTML that you can preview and embed. ChatGPT and Claude can both generate complete HTML with CSS styling.
Step 3: Preview and Refine
The AI will generate code. You can ask it to make the visualization:
- More colorful
- Mobile-responsive
- Sortable or interactive
- Matching your brand colors
- Include hover effects
Step 4: Copy and Embed
Once you're happy with the preview:
- Copy the generated HTML code
- Paste directly into your blog's HTML editor
- The styling is included, so it works immediately
Types of HTML Visualizations to Use
Comparison Tables
Perfect for: Product comparisons, feature matrices, pricing tiers, tool evaluations
Timeline Graphics
Perfect for: Historical context, process steps, development stages, roadmaps
Feature Matrices
Perfect for: Detailed product comparisons, capability assessments, decision-making
Pricing Calculators
Perfect for: Cost comparisons, ROI demonstrations, budget planning
Interactive Checklists
Perfect for: Step-by-step guides, implementation plans, assessment tools
Progress Indicators
Perfect for: Maturity models, skill assessments, implementation stages
Infographic-Style Layouts
Perfect for: Statistics, data points, key takeaways, visual summaries
Example Prompt and Result
Your Prompt to AI:
"Create an HTML comparison table for 5 email marketing platforms: Mailchimp, ConvertKit, ActiveCampaign, Klaviyo, and Sendinblue. Include columns for: Starting Price, Best For (use case), Key Features (3-4 bullets), and Free Tier (yes/no with limits). Make it visually clean with alternating row colors, responsive design, and hover effects. I want to be able to preview and embed this directly."
What You'll Get:
A complete HTML table with CSS styling that you can immediately embed in your article. The AI handles all the formatting, making it look professional without any design work on your part.
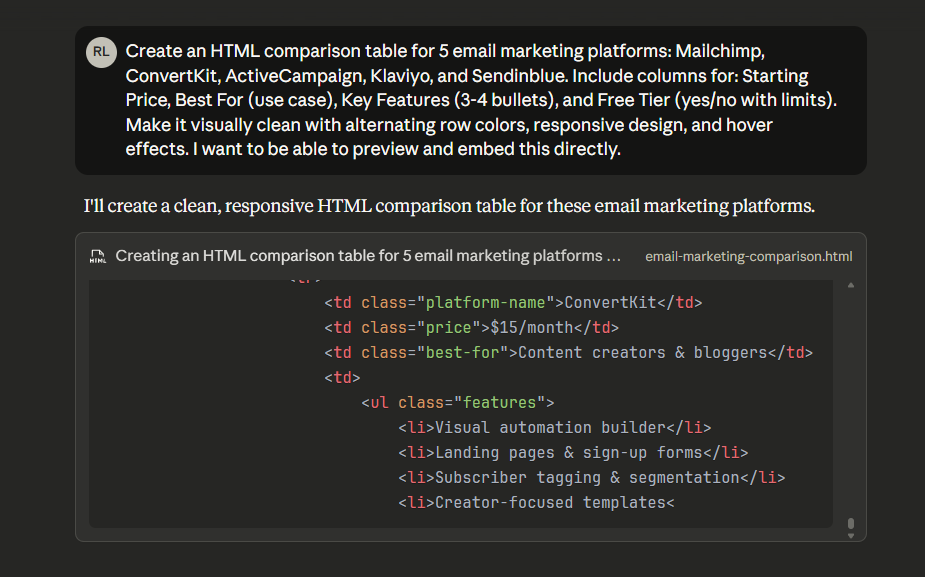
Using Claude.ai to generate an HTML template for a blog article
Phase 5: Internal Linking
Don't forget to link to your other relevant content. Internal links:
- Provide additional context for readers
- Help AI engines understand your content ecosystem
- Distribute authority across your site
- Encourage deeper engagement
Best practices:
- Link naturally within the content, not just at the end
- Use descriptive anchor text (not "click here")
- Link to 2-5 related articles
- Ensure links are contextually relevant
Example: "For more on building community engagement, see our guide to [creating meaningful virtual events]."
Quality Checklist Before Publishing
Before you hit publish, verify:
- Fresh date is prominently displayed
- H1 matches your target question
- H2 structure is clear and descriptive
- Bullet points break up dense sections
- FAQ section addresses related questions
- TL;DR provided (if title is a question)
- At least one HTML visualization included
- Internal links to related content (2-5 links)
- Differentiation strategy is clearly evident
- Your unique expertise shines through
- Mobile-responsive formatting
- No spelling or grammar errors
Step 8: Submission & Distribution
You've created your masterpiece. Now you need to make sure search engines and AI platforms know it exists.
Submit to Search Engines
Don't wait for search engines to eventually discover your content. Proactively submit it.
1. Google Search Console
Steps:
- Log into Google Search Console
- Navigate to "URL Inspection" in the left sidebar
- Enter your new article's URL
- Click "Request Indexing"
Google will typically index within 24-48 hours for new content on established sites. New sites may take longer.
2. Bing Webmaster Tools
Don't skip Bing. While it has less search volume than Google, sometimes it's easier to rank on and feeds into other platforms.
Steps:
- Log into Bing Webmaster Tools
- Navigate to "URL Submission"
- Enter your URL
- Submit
Bing often indexes faster than Google for new content.
3. Perplexity Pages (If You're a Subscriber)
This is a unique opportunity for Perplexity optimization.
If you're a Perplexity Pro subscriber, you can create Perplexity Pages—essentially summaries that link back to your full content.
Steps:
- Create a Perplexity Page summarizing your article
- Include key points and insights
- Link to your full article for "more details"
- This increases your visibility within the Perplexity ecosystem
Benefits:
- Your content gets exposure directly in Perplexity
- You're establishing authority on the topic
- Creates an additional pathway for citations
- Signals to Perplexity that you're creating valuable content
Distribution Beyond Search Engines
While not strictly part of GEO, consider:
Social Media: Share your article on relevant platforms where your audience spends time
Email Newsletter: Send to your subscribers if you have a list
Relevant Communities: Share in niche forums, Slack groups, or Reddit (following community rules)
LinkedIn: Particularly effective for B2B content
The more initial engagement your content gets, the stronger the signal to both search engines and AI platforms that it's valuable.
Step 9: Build Authority Through Backlinks (Optional)
Backlinks remain a factor in GEO, but their importance varies significantly by AI engine. Let's be realistic about what's achievable.
Why Backlinks Still Matter
Backlinks signal to AI engines that other sources consider your content credible and valuable. They're essentially votes of confidence from other websites.
However, the impact is different across platforms:
ChatGPT/SearchGPT: Tends to rely more heavily on established domains with strong backlink profiles. If you're targeting ChatGPT, backlinks matter more.
Perplexity: Actively diversifies sources and gives opportunities to quality content from newer or lower-authority sites. Backlinks help, but they're not make-or-break.
The Research: Our analysis of AI citation patterns shows that Perplexity actively diversifies while ChatGPT demonstrates a stronger preference for high-authority domains. (Read more in our AI Citation Patterns 2025 Analysis)
The Reality Check: This Is Challenging
I won't lie to you: getting backlinks is hard. Cold outreach to third-party websites has a low success rate. Most sites won't link to you just because you asked nicely and many of them might ask you to pay.
Strategies That Actually Work
1. Leverage Existing Relationships
The easiest backlinks come from people who already know and trust you:
- Business partners
- Customers or clients (case studies)
- Professional network contacts
- Past collaborators
- Industry peers
2. Guest Posting on Relevant Sites
If you can afford, write valuable content for other publications in your industry, and include a contextual link back to your article.
Keys to success:
- Choose sites your target audience actually reads
- Pitch useful article ideas, not thinly veiled ads
- Include the link naturally within the content, not just author bio
- Focus on 1-2 high-quality publications, not dozens of low-quality ones
Avoid:
- Buying links (can harm your rankings)
- Participating in link schemes or exchanges
- Spammy blog comment links
- Low-quality directory submissions
- Irrelevant guest posting just for the link
- Aggressive outreach campaigns that damage relationships
Remember: One quality backlink from a relevant, respected source is worth more than 100 low-quality links from random blogs.
If you secure 1-2 quality backlinks within 3 months, you're doing well.
The Bottom Line
Don't obsess over backlinks at the expense of creating great content. In the GEO landscape, particularly for Perplexity, differentiation often trumps domain authority.
For more on this principle, see our article on Differentiation vs Optimization in AI Rankings.
Step 10: Monitor Performance
GEO is a long-term strategy, and monitoring your performance is how you learn what works and double down on success.
Setting Realistic Timeline Expectations
First, manage your expectations:
First results: 1-2 months minimum
Meaningful traction: 3-6 months
Significant impact: 6-18 months
Free Method: Google Search Console
If you're on a budget, Google Search Console (GSC) is your best friend. It's completely free and provides valuable insights.
What to track in GSC:
- Impressions: How many times your page appeared in search results
- Clicks: How many people actually clicked through
- Position: Your average ranking position
- Queries: What search terms triggered your content
Advanced Monitoring Tools
For more sophisticated tracking—especially for AI-specific citations—consider these tools: Savannabay, Profound, Relens, Baby, Rank
Investment consideration: These tools typically cost $50-$500/month depending on features. Start with Google Search Console if budget is tight, then upgrade as you see traction.
Key Metrics to Track
Beyond basic analytics, focus on these GEO-specific metrics:
1. Citation Rate
What it is: Are you being mentioned/cited at all in AI responses to your target questions?
How to track:
- Manual testing (Temporary Chat mode)
- AI monitoring tools
- Regular queries of your target questions
What to look for: Percentage of your target questions where you get cited
2. Market Share Per Q&A Set
What it is: For a given question, what percentage of the time are you cited versus competitors?
Example: If the question "How to treat mild scalp psoriasis at home" gets asked 100 times and you're cited 35 times, your market share is 35%.
What to look for: Growing market share over time
3. Market Share Growth
What it is: Is your citation frequency increasing month-over-month?
How to track: Compare market share across time periods:
- Week 1-4 vs Week 5-8
- Month 1 vs Month 2 vs Month 3
What to look for: Upward trend indicating improving performance
4. Cluster Performance Analysis
What it is: Analyzing all related Q&A sets as a group
Components:
- Volume for the topic cluster
- Difficulty across related questions
- Your market share across the entire cluster
- Identification of high-opportunity questions you're missing
Why it matters: One article might target multiple related questions. Understanding cluster performance helps you identify content gaps and expansion opportunities.
5. Market Share Per LLM
What it is: Your performance broken down by AI engine
Track separately:
- ChatGPT citation rate
- Perplexity citation rate
- Gemini citation rate
- Claude citation rate
- Grok citation rate
Why it matters: You might perform well in Perplexity but poorly in ChatGPT. This tells you where to focus optimization efforts.
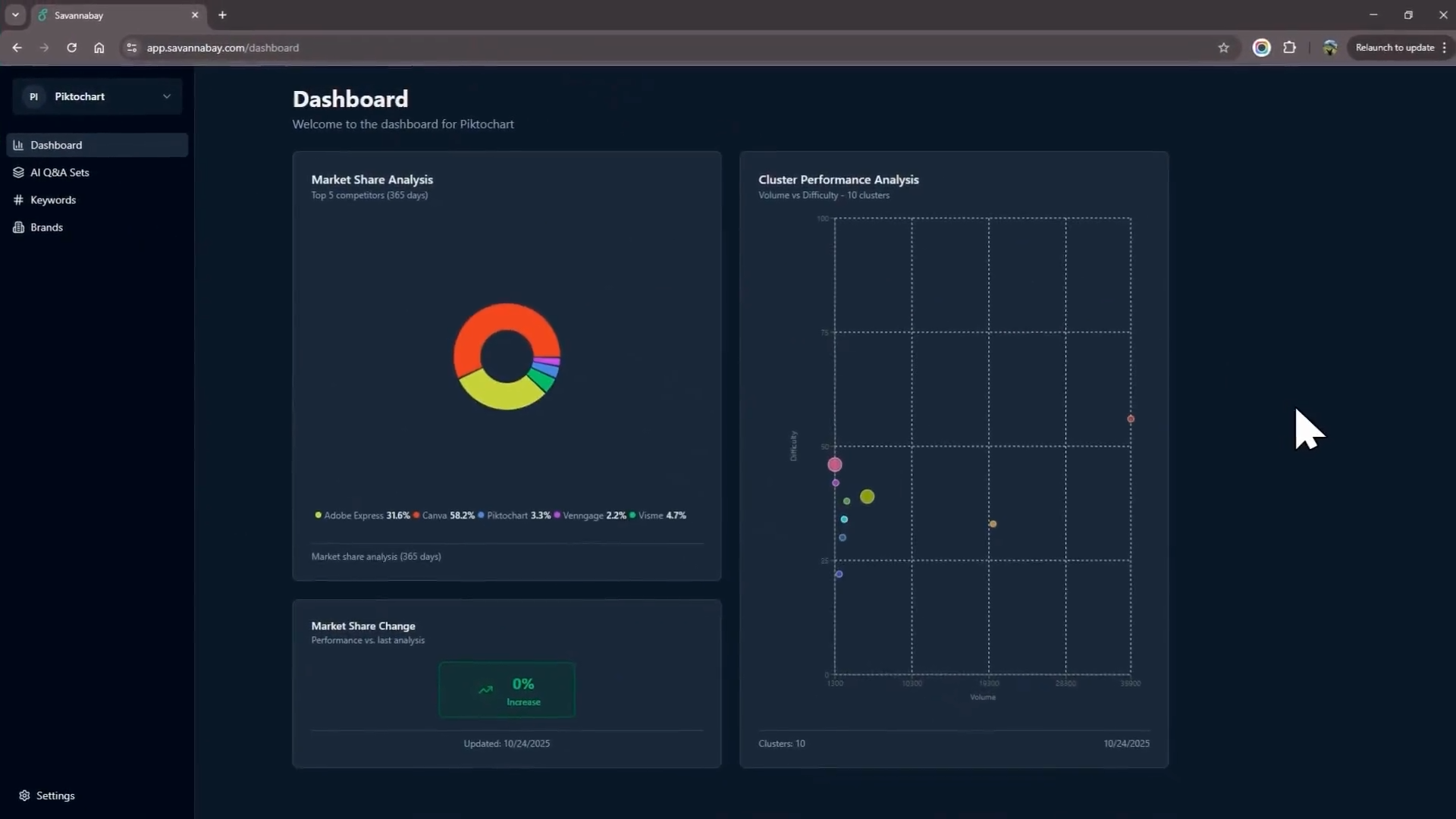
Example of GEO tool for monitoring AI citations
Common Mistakes to Avoid
You now have a complete framework for GEO success. But before you start executing, let's address the three mistakes that derail most GEO efforts.
Mistake #1: Semantic Copying Instead of Strategic Differentiation
What it looks like:
- Reading the top-cited article and rewriting it in your own words
- Making minor semantic changes but keeping the same structure and points
- Adding a few extra paragraphs and calling it "more comprehensive"
- Using synonyms but covering identical ground
Why it fails:
AI engines don't reward slightly different versions of existing content. If your article is semantically similar to what's already ranking—same points, same angle, same structure—you're competing directly with established, high-authority sources.
You will lose that fight.
The fix:
Return to Step 6 and genuinely find a differentiation strategy. Ask:
- What perspective is completely missing?
- What sub-topic deserves its own deep dive?
- What can I add from my unique experience that nobody else has?
- What format would serve this information better?
Real example of the difference:
Semantic copy (wrong): Everyone writes about "10 best project management tools" → You write "Top 12 project management software solutions for teams"
Strategic differentiation (right): Everyone writes general comparisons → You write "Project management tools for creative agencies that bill hourly: Time-tracking integration comparison"
The second approach targets a specific niche with a specific need that general comparisons don't adequately address.
Mistake #2: Chasing Low-Volume Keywords
What it looks like:
- Getting excited about difficulty 5 keywords without checking volume
- Targeting hyper-specific questions that 10 people per year ask
- Writing content for keywords with 0-50 monthly searches
- Prioritizing "easy wins" that don't move the needle
Why it fails:
Content creation takes real time and effort. Even with AI assistance, research, writing, editing, creating visualizations, and promotion require hours of work.
If you invest 5 hours into content that targets a keyword with 20 monthly searches, even capturing 100% market share nets you 20 visits per month. That's 240 visits per year for 5 hours of work.
The math doesn't work. I've spent a lot of time writing quality content that nobody has seen because the search volume was minimum.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How long does it take to see results from GEO?
A: Expect 1-2 months for initial results and 6-18 months for meaningful traction. Just like SEO, GEO is fundamentally a long-term strategy that rewards consistency and patience.
Q: Do I need a high domain authority to rank in AI results?
A: Not necessarily, but it helps. Our research shows that differentiation strategy often matters more than domain authority. A well-positioned article on a lower-DR site with unique insights can outperform generic content from high-DR sites.
Here's the nuance:
For ChatGPT/SearchGPT: Domain authority carries more weight. These platforms tend to rely more on established, high-authority sources.
For Perplexity: Actively diversifies sources and gives opportunities to quality content from newer or lower-authority sites. A DR 30 site with genuinely unique insights can outrank a DR 70 site with generic content.
Q: Can I use AI to write my entire article?
A: Yes, you can use AI to write your article, but here's the critical distinction: your unique expertise and perspective are what win citations.
What AI cannot do:
- Provide your unique insights and experience
- Share proprietary data or original research
- Offer the specific expertise that differentiates your content
- Create the strategic positioning that wins in competitive spaces
- Orchastrate the content and the pace of the story
The core value, unique angle and expertise must come from you.
Q: How important are backlinks for GEO?
A: Backlinks still matter, but their impact varies significantly by AI engine. Our research shows important differences:
Perplexity actively diversifies sources, giving opportunities to newer or lower-authority sites with quality content. While backlinks help, they're not make-or-break. A well-differentiated article on a site with few backlinks can still get cited if it offers unique value.
ChatGPT (especially via SearchGPT) tends to rely more on established domains with strong backlink profiles. If you're targeting ChatGPT, backlinks carry more weight in your overall strategy. For more detailed analysis, see our research on AI Citation Patterns.
The practical strategy:
- Focus on creating differentiated content first (Steps 1-7)
- Publish and submit to search engines (Step 8)
- Then pursue 1-2 quality backlinks per article, but keep in mind it's not easy at all.
Overall, don't let lack of backlinks stop you from publishing.
Q: What's the difference between GEO and traditional SEO?
A: They're very similar and share the same core principles—especially E-E-A-T (Experience, Expertise, Authoritativeness, Trustworthiness). The strategy is essentially the same these days, particularly because Google already answers questions with AI-generated overviews. SEO traditionally is based on keyword research and monitoring while GEO is based on questions.
The main differences:
1. Monitoring and Metrics
- Traditional SEO: Track rankings (position 1-10), clicks, impressions
- GEO: Track citations, market share per Q&A set, performance across AI engines
2. Citation vs. Ranking
- Traditional SEO: Goal is to rank #1 for a keyword
- GEO: Goal is to be cited in AI responses (can be cited even if not #1 in traditional search)
The core similarities:
- Both focus on quality, authoritative content
- Both value E-E-A-T signals
- Both benefit from good technical SEO (fast loading, mobile-friendly)
- Both require understanding user intent
- Both reward original, valuable content over thin content
Q: Is it worth adding the year (like "2025") to my content?
A: Absolutely. Year-specific content creates multiple advantages:
Triggers SearchGPT: When users include a year in their query (e.g., "best CRM in 2025"), ChatGPT often activates SearchGPT to pull current information rather than relying solely on training data.
Signals Freshness: AI engines favor recent content, especially for topics where information changes. Adding the year makes it crystal clear your content is current.
Matches User Intent: People asking year-specific questions want up-to-date information, not content from 2022. Your title and fresh date signal you're providing exactly what they need.
Q: Should I focus on one AI engine or try to rank in all of them?
A: Focus on one primary AI engine (ChatGPT or Perplexity recommended), but your content will likely impact multiple engines.
Don't: Try to win in all five engines at the same time from day one. You'll spread yourself too thin and won't understand what's actually working.
Q: How much should I invest in GEO tools and monitoring?
A: Start free, then upgrade based on results and ROI.
Month 1-3 (Free tier):
- Google Search Console (free)
- Manual testing via Temporary Chat (free)
- Spreadsheet tracking (free)
- Total cost: $0
Month 4-6 (If seeing traction):
- Continue free tools
- Add one monitoring tool trial (Savannabay, Baby)
- Evaluate if the insights justify the cost
- Total cost: $0-50/month
Month 7-12 (If showing ROI):
- Invest in one comprehensive monitoring tool ($50-200/month)
- Consider keyword research tool subscription if not already using (Ahrefs/SEMrush: $100-200/month)
- Total cost: $150-400/month
Ready to start using this framework? Begin with Step 1 and let us know your results.
Last Updated: November 21, 2025